SAELens v6
SAELens 6.0.0 is live with changes to SAE training and loading. Check out the migration guide →
SAELens
The SAELens training codebase exists to help researchers:
- Train sparse autoencoders.
- Analyse sparse autoencoders and neural network internals.
- Generate insights which make it easier to create safe and aligned AI systems.
Quick Start
Installation
Loading Sparse Autoencoders from Huggingface
To load a pretrained sparse autoencoder, you can use SAE.from_pretrained() as below:
from sae_lens import SAE
sae = SAE.from_pretrained(
release = "gemma-scope-2b-pt-res-canonical",
sae_id = "layer_12/width_16k/canonical",
device = "cuda"
)
You can see other importable SAEs on this page.
Any SAE on Huggingface that's trained using SAELens can also be loaded using SAE.from_pretrained(). In this case, release is the name of the Huggingface repo, and sae_id is the path to the SAE in the repo. You can see a list of SAEs listed on Huggingface with the saelens tag.
Loading Sparse Autoencoders from Disk
To load a pretrained sparse autoencoder from disk that you've trained yourself, you can use SAE.load_from_disk() as below.
Importing SAEs from other libraries
You can import an SAE created with another library by writing a custom PretrainedSaeHuggingfaceLoader or PretrainedSaeDiskLoader for use with SAE.from_pretrained() or SAE.load_from_disk(), respectively. See the pretrained_sae_loaders.py file for more details, or ask on the Open Source Mechanistic Interpretability Slack. If you write a good custom loader for another library, please consider contributing it back to SAELens!
Model Compatibility
SAELens SAEs are standard PyTorch modules and work with any framework or model architecture, not just TransformerLens. While SAELens provides deep integration with TransformerLens through HookedSAETransformer, you can use SAEs with:
- Hugging Face Transformers: Extract activations using PyTorch hooks and pass them to
sae.encode()/sae.decode() - nnsight: Use nnsight's tracing API for clean intervention patterns with SAE features
- Any PyTorch model: SAEs work on any tensor with the correct input dimension
The core SAE methods (encode, decode, forward) accept standard PyTorch tensors, making them compatible with any activation extraction method.
import torch
from sae_lens import SAE
sae = SAE.from_pretrained(
release="gemma-scope-2b-pt-res-canonical",
sae_id="layer_12/width_16k/canonical",
device="cuda"
)
# SAEs work with any activation tensor of the right shape
# Gemma 2 2B has d_model=2304
activations = torch.randn(1, 128, 2304, device="cuda") # From any source
features = sae.encode(activations)
reconstructed = sae.decode(features)
For detailed examples including Hugging Face and nnsight integration, see the Usage Guide.
Background and further Readings
We highly recommend this tutorial.
For recent progress in SAEs, we recommend the LessWrong forum's Sparse Autoencoder tag
Tutorials
Below are some tutorials that show how to do some basic exploration of SAEs:
- Loading and Analysing Pre-Trained Sparse Autoencoders
- Understanding SAE Features with the Logit Lens
- Training a Sparse Autoencoder
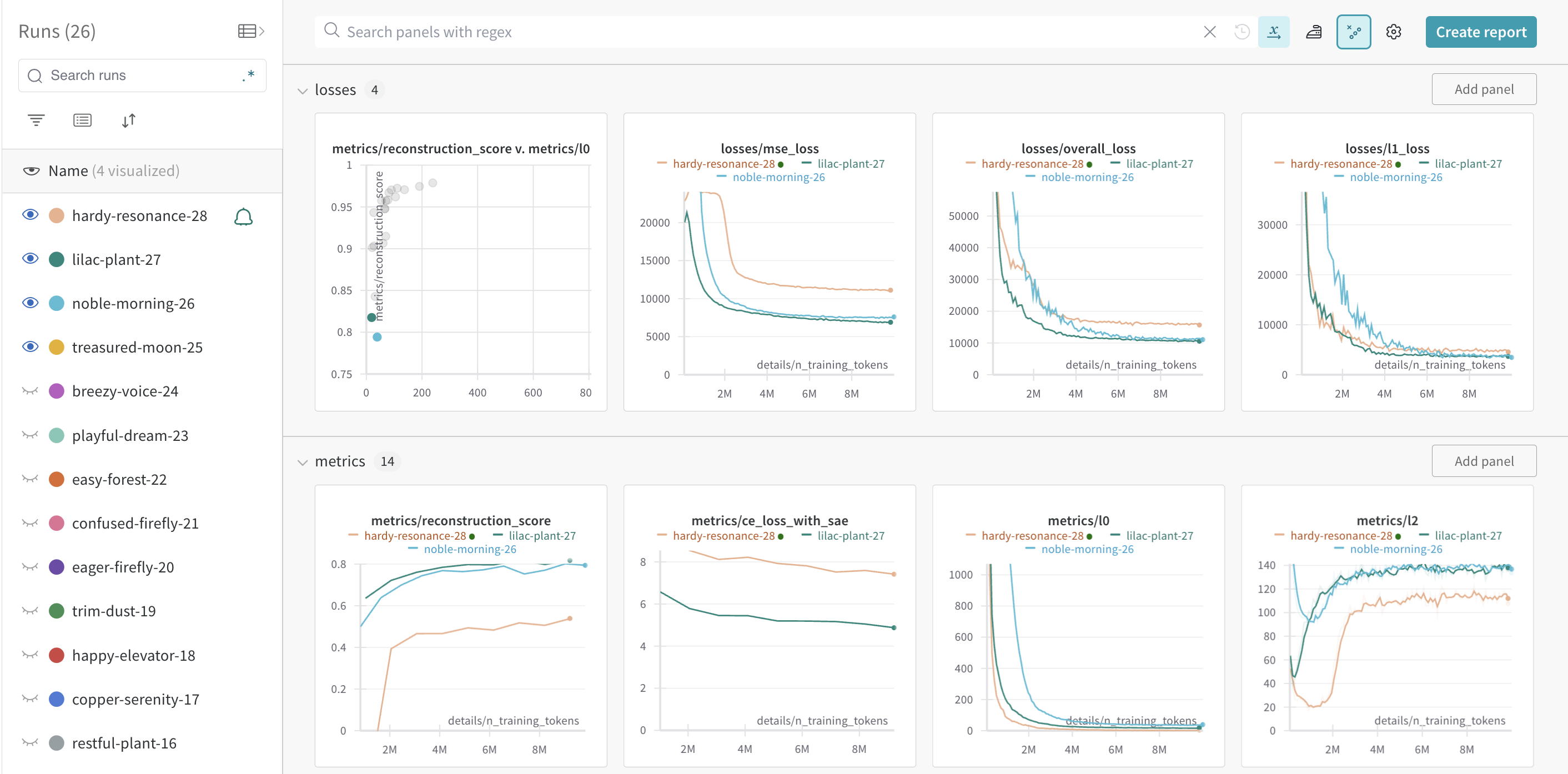
Example WandB Dashboard
WandB Dashboards provide lots of useful insights while training SAEs. Here's a screenshot from one training run.